Biology Escape Room
Review of Food Webs and Food Chains
Digital Escape Room Link
Dr. Gayden's Biology Class
Saturday, April 13, 2019
Monday, February 4, 2019
Tuesday, January 29, 2019
January 29, 2019
ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What is the purpose of the Immune System?
LEARNING TARGET: Summarize the basic functions of the human immune system, vaccines, and antibiotics
BENCHMARKS: SC.912.L.14.52
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to:
-Summarize the basic functions of the human immune system.
-Compare and contrast types of infectious agents that may infect the human body.
BELL RINGER - EOC Focus Review: SC.912.L.14.36 Blood
Flow
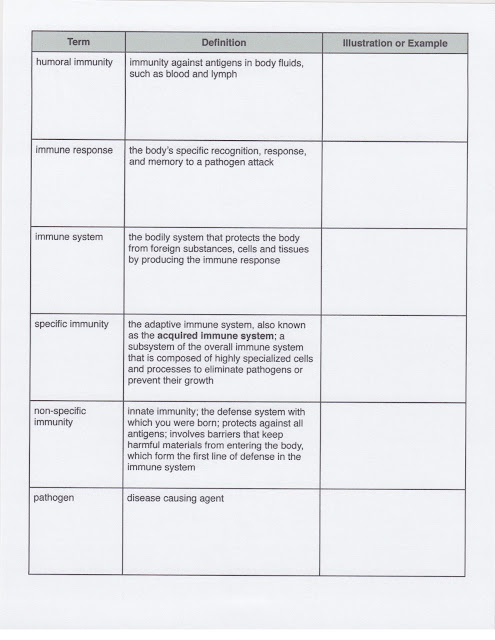
VOCABULARY: antibiotics, antibody, antigen, allergy, cell-mediated immunity, B cells, T cells, chronic disease, communicable disease, humoral immunity, immune response, immune system, specific immunity, nonspecific immunity, infectious agent, pathogen, vaccines, fever, white blood cells, macrophages, histamines, antihistamines
HOME LEARNING: HL 2: Primary and secondary immune response
AGENDA
WHOLE GROUP
Students completed the bell ringer above.
Students then received the vocabulary terms below. For each term, students should illustrate or write an example to help them remember the terms. Students also received Frayer word maps as home learning with specific words to map out.
Engage: Reflect on the following
A. What are some examples of organisms that cause disease?
B. What are some ways diseases are spread?
C. What are some ways we can prevent the spread of diseases?
D. Why do you think the human body makes a great place for disease causing organisms to grow?
E. In spite of being under constant attack by pathogens, we do not get sick all the time. What organ system is responsible for this?
-Explain to students that normally the body’s immune system protects them against
disease.
Video: Bob's Germs go to work
We then watched the video Bob's Germs Go To Work to introduce the topic of the Immune System. You can watch the film below.
Explore: GIZMO Pathogen spread
Explain: Notes - Immune System
You can find them below.
Evaluate: HL 2 Primary and secondary immune response
Exit Strategy: Write to explain why it is necessary to get your child immunized
H.O.T. QUESTIONS:
1. Why do you think is a beneficial adaptation for a pathogen to make its host very sick without killing the host? The pathogen often needs the host to stay alive for the pathogen to reproduce or replicate. A sick host is beneficial for the pathogen if some of the host’s behaviors, such as coughing and sneezing, helps spread the
pathogen.
2. Animals infected with the virus that causes rabies often salivate excessively and are apt to bite other animals even when unprovoked. How do these symptoms lead to the spread of the virus? The virus is probably present in the saliva. When an infected animal bites another animal, the pathogen in the infected animal’s saliva comes in contact with the bitten animal’s blood.
3. In what ways are symbiotic organisms that live on or in the human body similar to pathogens that make take up residence? How are they different? They are similar in that both require the human body to carry out their life cycles. They are different in that symbiotic organisms are generally harmless or may be beneficial to
humans, while pathogens cause diseases.
You can find them below.
Thursday, December 13, 2018
Tuesday, October 16, 2018
Thursday, May 10, 2018
Monday, December 18, 2017
Monday, 18 December through Friday, 22 December, 2017
NOTE: Due to Holiday Activities, class did not meet each day for for the entire class period on the days we did have class. Therefore some activities were not completed and will be completed next class period.
ESSENTIAL QUESTION: What is the purpose of the Immune System?
LEARNING TARGET: Summarize the basic functions of the human immune system, vaccines, and antibiotics
BENCHMARKS: SC.912.L.14.52
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to:
-Summarize the basic functions of the human immune system.
-Compare and contrast types of infectious agents that may infect the human body.
Bell Ringer: The diagram below represents possible evolutionary pathways of certain organisms.
Which species is most closely related to species L?
A. Species E
B. Species F
C. Species G
D. Species I
VOCABULARY: antibiotics, antibody, antigen, allergy, cell-mediated immunity, B cells, T cells, chronic disease, communicable disease, humoral immunity, immune response, immune system, specific immunity, nonspecific immunity, infectious agent, pathogen, vaccines, fever, white blood cells, macrophages, histamines, antihistamines
HOME LEARNING: notebook update
AGENDA
WHOLE GROUP
Students completed the bell ringer question and justified their answer.
Students then took notes on the immune system. The powerpoint movie of the notes is included below.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)