ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How can populations evolve to form new species?
NGSSS: SC.912.L.15.13; SC.912.L.15.15; A.912.L.15.15
BENCHMARKS:
-Describe the conditions required for natural selection, including: overproduction of offspring, inherited variation, and the struggle to survive, which result in differential reproductive success. -Discuss mechanisms of evolutionary change other than natural selection such as genetic drift and gene flow.- Describe how mutation and genetic recombination increase genetic variation.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Students will be able to:
-identify the conditions required for natural selection.
-relate the conditions required for natural selection to differential reproductive successes.
-recognize some of the scientific mechanisms resulting in evolutionary change.
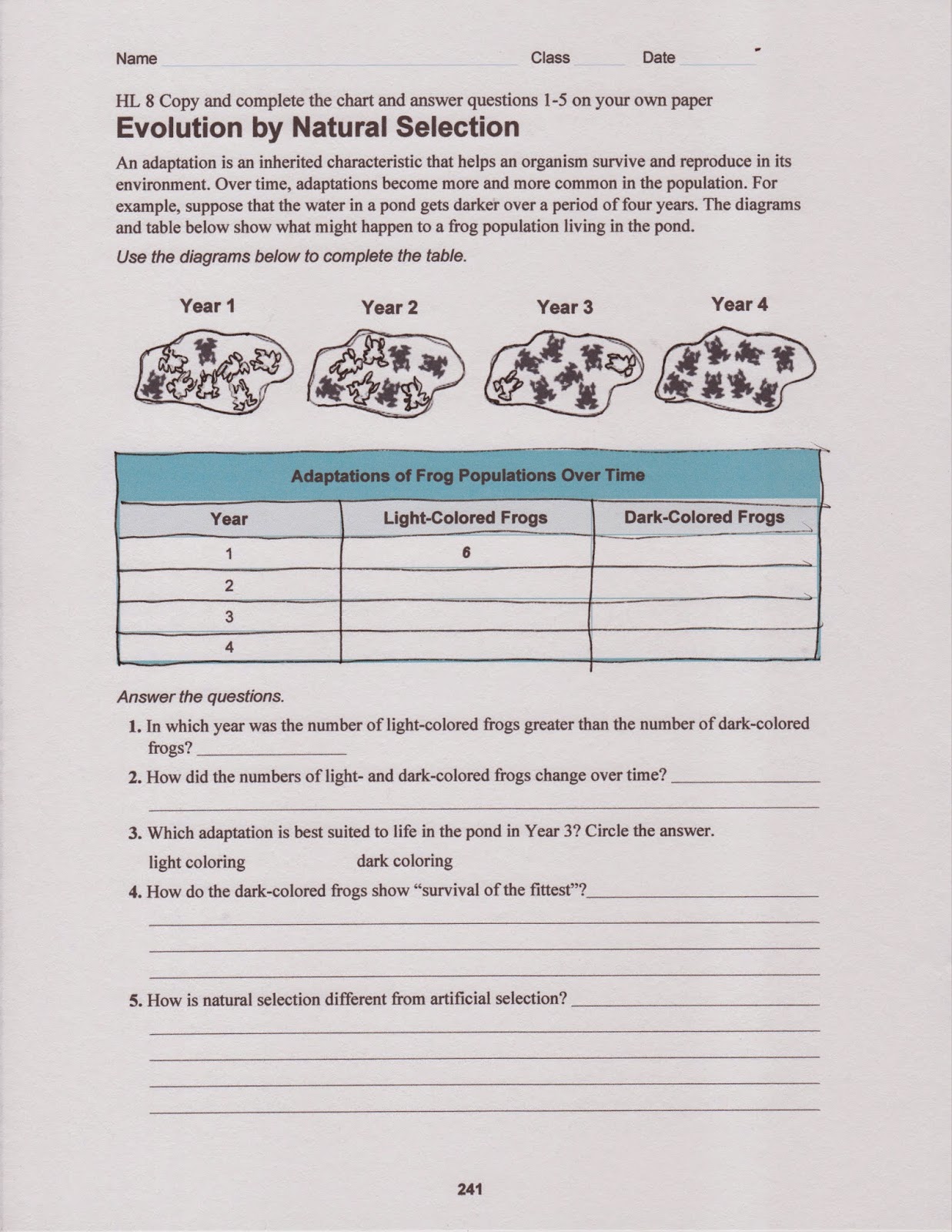
BELL RINGER: Answer the questions on the handout. Place the completed handout in your notebook. You will use the handout to enter your answers using the CPS clicker system. I apologize that I am not able t add the handout to this lesson. My regular computer is down and I cannot access my scanner to scan in the appropriate handout.
VOCABULARY: adaptation, adaptive radiation, ancestor, artificial selection, bottleneck, coevolution, convergent evolution, directional selection, disruptive selection, evolution, extinction
HOME LEARNING: Study for Mid-year Biology Exam
Students completed the handout and reviewed the information, which will help prepare you for the Winter interim assessment in biology, to be given next week.
We then completed the questions from the Peppered Moth Simulation. You can find the activity on Dr. Gayden's Science Zone. Next class, we will do the actual experiment.